The HEXUS editor provided a deep dive into AMD Epyc Rome CPU architecture and the Epyc 7002 Series of processors in our review of the AMD Epyc 7742 2P Rome Server back in August. If you have pondered over this detailed review you will already have good insight into how the Epyc Rome processors are put together, their essential components, chiplets structure and other details of AMD's implementation.
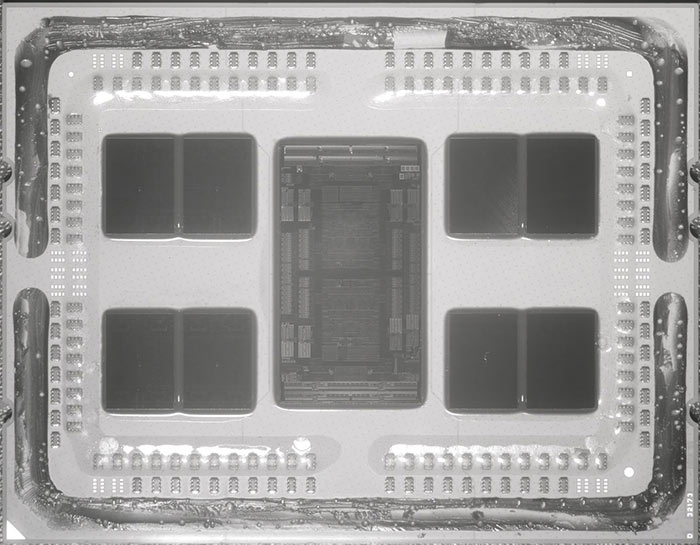
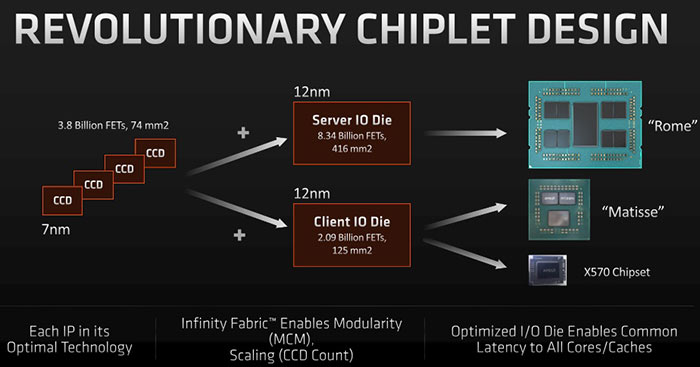
Some new hugely detailed images of an AMD Epyc Rome IOD (Input/Output Die) with its 8.34bn transistors have recently been shared by HardwareLuxx forum user OC_Burner. With this IOD plus 8x CCDs an Epyc Rome processor contains 39.54bn transistors. The nine dies are connected together on a chip that measures 1,008mm2.
The above numbers seem huge, but they are more illuminating if we compare these vital statistics to previous products, some of which you might know well.
|
Comparison of fabrication, size and number of transistors |
||
|
|
The size |
transistors |
|
Zen (Zeppelin) |
212 mm² |
4.8 billion |
|
Zen + (Zeppelin) |
212 mm² |
4.8 billion |
|
CCD (Matisse & Rome) |
74 mm² |
3.9 billion |
|
IOD (Matisse) |
125 mm² |
2.09 billion |
|
IOD (Rome) |
416 mm² |
8.34 billion |
|
Matisse in total: 2x CCD + IOD |
273 mm² |
9.89 billion |
|
Rome in total: 8x CCD + IOD |
1,008 mm² |
39.54 billion |
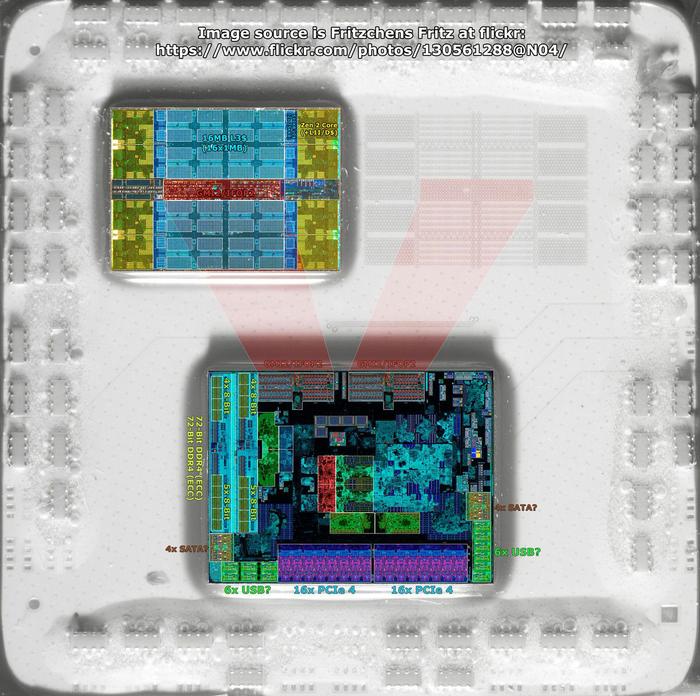
In addition to the overview shot, top, which is taken with the Rome chip bathed in IR light, under which silicon is semi transparent, there are some highlighted 'dyed' shots shared by Twitter user Locusa. Below you can see this analysis which has highlighted key components such as L3 cache, CPU cores, plus DDR4 and PCIe interfaces.
Click to zoom image
Rome has a much larger IOD at 416mm2 (though shares the same CCDs as Matisse) and it features 128x PCIe Gen 4 lanes, as well as 8x DDR4 memory interfaces. Additionally in turquoise you can see some parts called GMI, which standard for Global Memory Interconnect, and HardwareLuxx explains that each of these creates "the interconnect to one CCD each of the Epyc processor".