Whats DDR?
The primary differences between SDRam and DDR ram is that DDR runs on a different voltage stepping. It runs at 2.5 rather than the 3.3 of current SDRam. DDR Ram is nothing "new" - we have seen it on graphics cards for a while now, but it is new to see this technology on a system board. DDR Ram uses 184 pin interfaces, rather than the 168 pin of normal SDRam. To stop people from putting the wrong memory in the wrong slots, they have moved a few pins around too.You can get DDR ram easily and cheaply now, and it comes in several different styles just like normal ram (unbuffered etc). There are also in 2 speeds, PC-1600 or PC-2100. The DDR modules will have higher capacity per DIMM. This is perfect for high-end servers, which need a high amount of main system memory, for example for large databases. Unfortunately this doesn’t benefit end-user systems as they don’t have any data buffers present on the memory module, and it will only handle lower capacities, usually up to 512MB per module. Because of this the AMD
761 chipset can only access 2GB of unbuffered Dimms.
For a more detailed explanation of DDR Technology check this writeup here.
AMD had an aim after releasing the first breed of Athlon of moving on to the new generation Socket At this point they decided to develop their own chipset, which was for the good as no-one liked using Via's chipset. The primary objective of AMD developing their chipset was to set a new level of memory standards. This was probably developed in direct competition to Intel and RamBus, and AMD wanted to develop this to put themselves on the high memory
bandwidth market. They want to increase the memory bandwidth, which is limited at 1GB/sec with PC133.
The new memory, PC-1600 and PC-2100, will run at twice the clock frequencies of the current PC-100, and 133 SDRam. The major differences between the 2 memory types (1600, and 2100) is that 1600 runs at 200MHz Clock, and the 2100 runs at 266 Clock. Conveniently DDR ram runs perfectly inline with the current setup
of AMD's newest series of Athlons CPUs, i.e. the DDR 1.2 Ghz unit. All the new upcoming processors will run at 266Mhz bus frequency and this is perfect for the
PC-2100 DDR Modules.
DDR Ram across the Motherboard

The Northbridge Chipset on this motherboard supports up to 4GBs of Ram. The AMD76x allows many features to be supported. for example ECC ram. This chipset can be switched between workstations and servers without any issues at all. One major glitch with it is that it doesn’t support Dual CPUs (while the AMD-760MP does.) There aren’t any incompatibilities with this motherboard it supports 4X AGP, and it will run any GeForce 2 based cards without an issue. The Southbridge (AMD-766) supports UDMA-100 and more USB features, both of which are things we have been taking for granted with Via Chipset boards. This board also supports the usual super bypass.
Motherboard showing NorthBridge
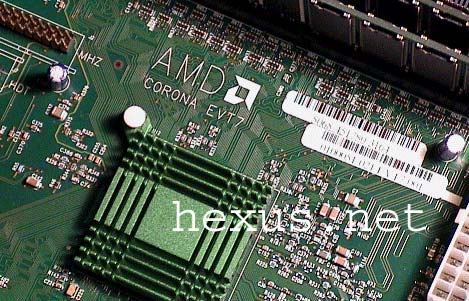
When AMD called us to tell us about the release of the 1.2 CPU, we were warned to hold off reviewing it as we had a system due to hit us soon which would blow our socks off. And they were right. With Intel releasing the P4s at high apparent clock speeds, AMD thought they would have a problem, but so far all the P4s have sucked - like the first round of Katmai
P3s really. Just wait though, I have been told some interesting stuff about Intel’s relationship
with another large company and lets just say it will change the way of the world.
The CPU :-

The System provided AMD
AMD 1.2 Ghz Thunderbird DDR CPU (Socket A, We have unlocked this)
256 MB PC-2100 DDR Ram (Micron / Crucial)
AMD EVT7 Corona Motherboard (Pre release)
It also came with other trimmings but we decided to test it with the usual Hexus kit, rather than using AMD’s.
As I mentioned above, we had to unlock the CPU ourselves, we did the usual pencil trick on it and it was unlocked within minutes.









